Affirm-AHF Trial
Overview & Conclusions
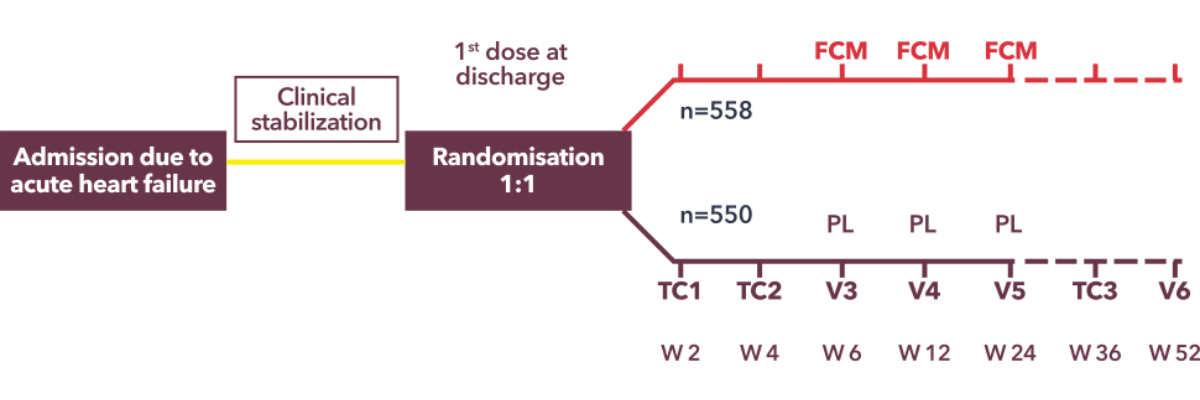
Affirm-AHF was designed assess intravenous ferric carboxymaltose among patients who were hospitalized for acute heart failure and iron deficiency. This was a randomized, parallel, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial done at 121 sites in Europe, South America, and Sigapore. The study design is described in the figure below.
Key
inclusion
Criteria
- Iron deficiency
serum ferritin < 100ng/mL or 100-300 ng/mL + TSAT<20% - LVEF<50%
- Hb 8 – 15 g/dL
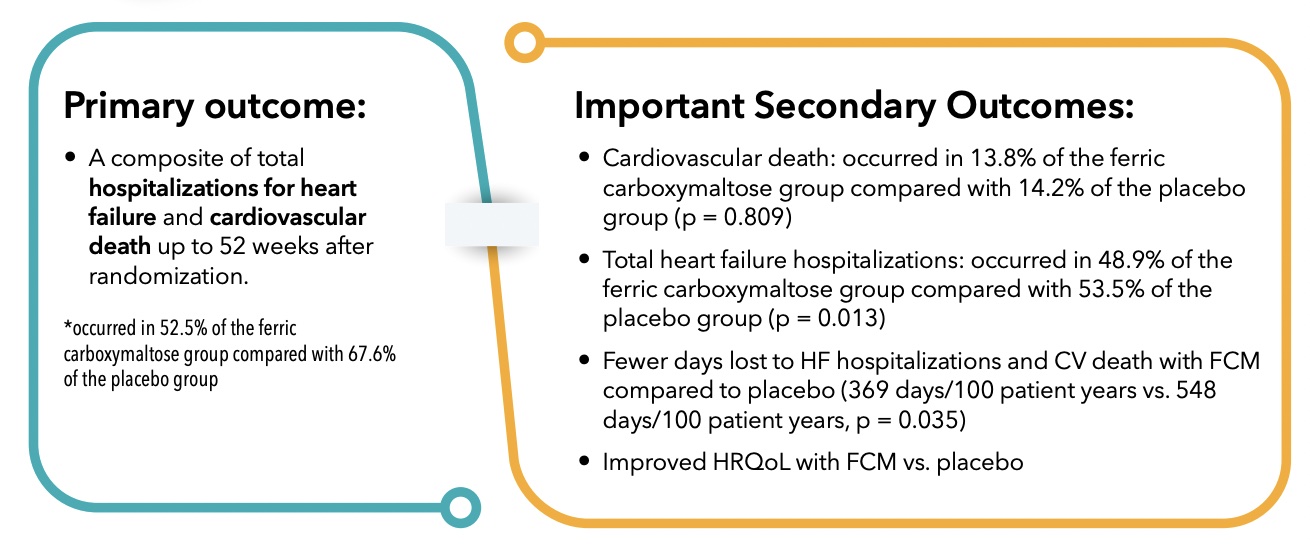
Primary outcome:
- A composite of total hospitalizations for heart failure and cardiovascular death up to 52 weeks after randomization.
*occured in 52.5% of the ferric carboxymaltose group compared with 67.6% of the placebo group.
Important Secondary Outcomes:
- Cardiovascular death: occured in 13.8% of the ferric carboxymaltose group compared with 14.2% of the placebo group (p = 0.809)
- Total heart failure hospitalizations: occured in 48.9% of the ferric carboxymaltose group compared with 53.5% of the placebo group (p = 0.013)
- Fewer days lost to HF hospitalizations and CV death with FCM compared to placebo (369 days/100 patient years vs. 548 days/100 patient years, p = 0.035)
- Improved HRQoL with FCM vs. placebo
Interpretations
In iron-deficient patients with heart failure (LVEF <50%), who were stabilized after an acute HF event, treatment with intravenous ferric carboxymaltose was associated with a significant reduction in total heart failure hospitalizations, as well as improved HRQoL compared with placebo.
Download this article as a PDF
FCM= FERRIC CARBOXYMALTOSE; PL = PLACEBO; HRQOL = HEALTH-RELATED QUALITY OF LIFE
REFERENCES:
Ponikowski, Piotr, et al. “Ferric carboxymaltose for iron deficiency at discharge after acute heart failure: a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, controlled trial.” The Lancet 396.10266 (2020): 1895-1904.
Jankowska, Ewa A., et al. “The effect of intravenous ferric carboxymaltose on health-related quality of life in iron-deficient patients with acute heart failure: the results of the AFFIRM-AHF study.” European Heart Journal (2021).